Marketers have the choice to specify and target specific or niche audiences in various ways. One of these ways is using geo-targeted ads, which play a vital role in PPC (pay-per-click) campaigns and deliver ads to people in specific areas. This is quite an effective strategy that can build brand awareness in any locality.
However, it is natural for companies to make geo-targeting mistakes, lessening the effectiveness of their campaigns. At its worst, it can result in the loss of potential customers. You must avoid some common Google Ads geo-targeting mistakes to prevent these from happening.
What is Geo-Targeting and How it Works
Before diving into the most common geo-targeting mistakes that can be done on Google Ads, let’s understand how geo-targeting works.
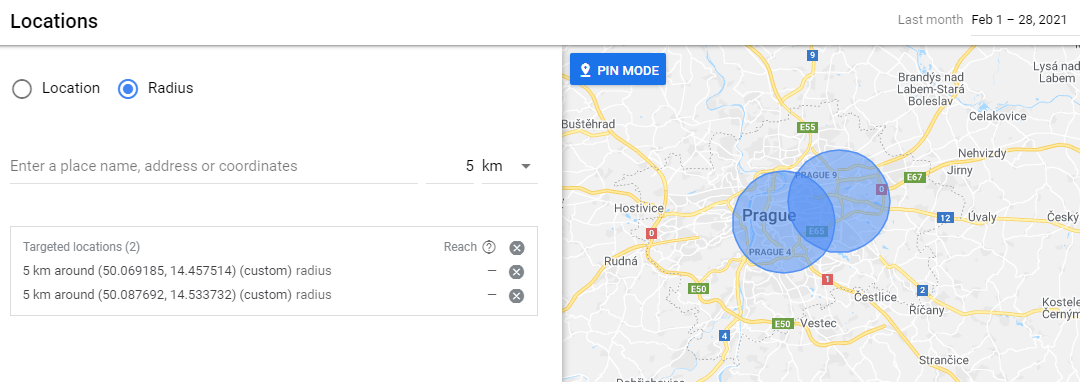
Google Ads has a feature that allows advertisers to set specific locations where they want their ads to be shown to users. This is an essential tactic for businesses, especially those that depend on home deliveries and/or foot traffic, such as e-commerce sites, brick-and-mortar stores, and restaurants.
In Google Ads, you have the option to configure the targeting settings according to different factors, such as:
- Nations
- Areas within the nation
- The radius of the location
- Specific location groups like business location, places of interest, etc.
The main benefit of geo-targeting in Google Ads is that displaying ads to non-relevant audiences will waste clicks and impressions, effectively cutting the marketing budget and not providing any return. Hence, geo-targeting is a helpful tool for many advertisers and marketers, provided they will avoid mistakes while setting it up.
11 Common Mistakes While Setting Up Geo-Targeting in Google Ads
#1: User Location and IP Address Mismatch
This is considered the most common mistake regarding geo-targeting in Google Ads. The IP (Internet Protocol) address is designated by the ISP (Internet Service Provider) to provide users’ location. This is how Google helps you decide where to show your ads, based on the ISP and IP of the customers.
However, Google has also admitted that the IP location may not be the same as the user location. While Google notes that you can put the target area/country/city in the ad, most marketers would agree that this method is not the most effective.
There are two main errors with this approach: the false positive and the false negative. False-positive means that you are not while you may appear in Los Angeles (for example). According to Google, false-negative is the invert of the former and means that while you may be in Los Angeles, you don’t appear to be. Hence, the credibility of this approach comes into play.
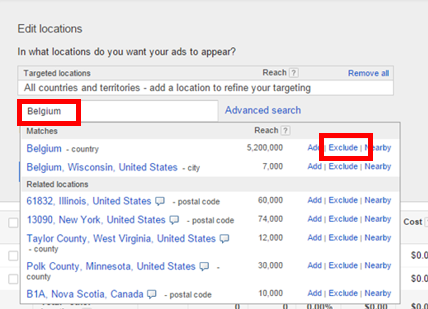
The practical solution here is to exclude specific locations. For instance, if you have a business selling clothes locally in London but are receiving many clicks from Sri Lanka, you may have to exclude that nation from your campaigns. However, be sure to do so carefully so that you don’t end up alienating potential customers.
#2: Not Being Specific in Terms of Location
When you operate a business online, you think—who needs boundaries? This thought seems reasonable at first—why stick with one location when you can create an ad and target everyone globally?
However, you must be specific when it comes to geolocation. Creating location-specific ads will get better engaged and more meaningful traffic. However, you should also know that specifying the target location can also take a lot of time, depending on the extent of your campaign. So why is it worth the hard work?
People from different locations will behave differently toward a particular business, service, or product. For instance, let’s say you have an online store that sells shoes for the winter. While you may garner many clicks from colder nations like Canada or Russia, you won’t have much luck with countries like Jamaica, which is hot and sunny year-round.
#3: Not Setting Up Location Exclusions
As mentioned above, you need to set up the proper location to ensure that your Google Ads target customers and clients within a specific location, not people merely showing interest. With this, you will ensure that the searches are more qualified and that your users are more engaged.
You need to look through the locations you are currently targeting. If you do not see the expected results, you should consider setting up exclusions. Of course, the results will vary from one location to another; hence, you should know the KPIs (key performance indicators) for each campaign you initiate.
It’s essential to set up exclusions within your Google Ads marketing campaigns. Let’s say you have a car dealership in Alaska. While your dealership is located on an international border, you can exclude Canada if you don’t do business internationally. In fact, you can exclude any location down to the zip code.
Experts recommend excluding major airports within the locations you are targeting. Most people in these locations are simply traveling through, and may be an ineffective use of impressions.
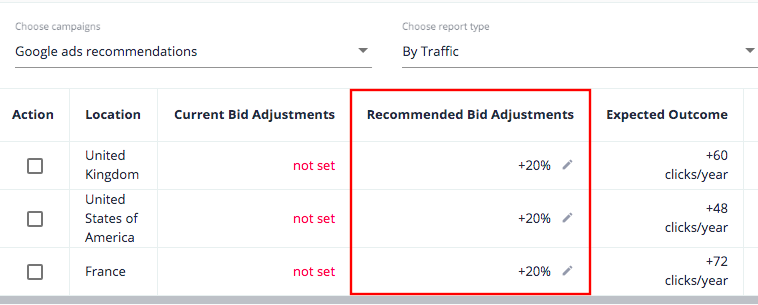
#4: Not Using Location Bid Adjustments
In most cases, different locations perform differently—some of them may convert better than others, although CPC may not vary drastically. For advertisers, it means that they pay more for conversions from the low-performing regions.
Location bid adjustments allow you to cut misused ad spending by reducing bids for low-performing locations and vice versa.
While adjusting bids, you should tackle two tasks: define low-performing locations and the exact adjustment values. You can carefully look through the Google Ads reports and iterate over various adjustment values, but the better way is to use the PromoNavi Location Bid Adjustment tool. It will provide you with a daily report of bid adjustments you need to make on your campaign for the best performance possible.
Here is a comprehensive manual on how to adjust bids by locations with the help of PromoNavi.
The PromoNavi Location Bid Adjustment tool is one of seven available campaign recommendations that will help you optimize your Google Ads campaign to drive more clicks and save your ad budget. For instance, you can also adjust bids for different devices, such as smartphones and computers, to ensure your advertising campaign is effective.
#5: Improper Audience Segmentation
When your business starts to grow and you add multi-location firms, it becomes crucial to segment your audiences into smaller, more manageable groups. This needs to be done so that your customers and clients respond better to relevancy.
For instance, while sending the same email to all your subscribers may seem fine, this approach will fall flat as you expand your business to more areas. Suppose your business is spread across multiple locations. In that case, the first thing you need to consider for geo-targeting is geography, as you would want to deliver the best services and products to local customers first.
However, this doesn’t mean that you stop at this point. As your market share increases, you can segment your audiences according to different categories like demographics, behavior, etc. The more you segment, the better responses, and engagement your marketing campaigns will have.
Let’s say that you have different sections in your local store. On the one hand, the men’s section is selling its goods, while the children’s and women’s sections are performing poorly. In this case, you need to study why the men’s section and children’s/women’s sections are inversely proportional to each other. Maybe you are selling men’s clothes that fit the region and not doing the same for the others. Hence, understanding and analyzing the audience in a particular location is important to your success and growth.
#6: Not Assessing Analytics for Each Location
Let’s say that one of your business locations has decided to sell winter clothes in the colder regions. That doesn’t mean you will sell these winter clothes in business locations situated in warmer places; this is simply a waste of energy, time, and money.
You cannot study the performance of your campaigns without diving deep into their analytics. Like other approaches, analyzing each location for a multi-location brand can be very difficult. Most would be content by only looking at the top-level results since these campaigns are much more complex, with more audiences, stores, outlets, offices, etc.
However, you must resist this temptation. There is more data to parse with multi-location marketing campaigns, meaning you have more to understand and take away. If you properly analyze the data, you will be able to confirm whether a particular idea or tactic has worked in a certain location or if a change in the ad’s wording has garnered higher conversion rates.
Analytics are valuable insights that you need to get into. If you are a savvy marketer, you will be rewarded for your analytic efforts in marketing your multi-location business with better engagement and conversion.
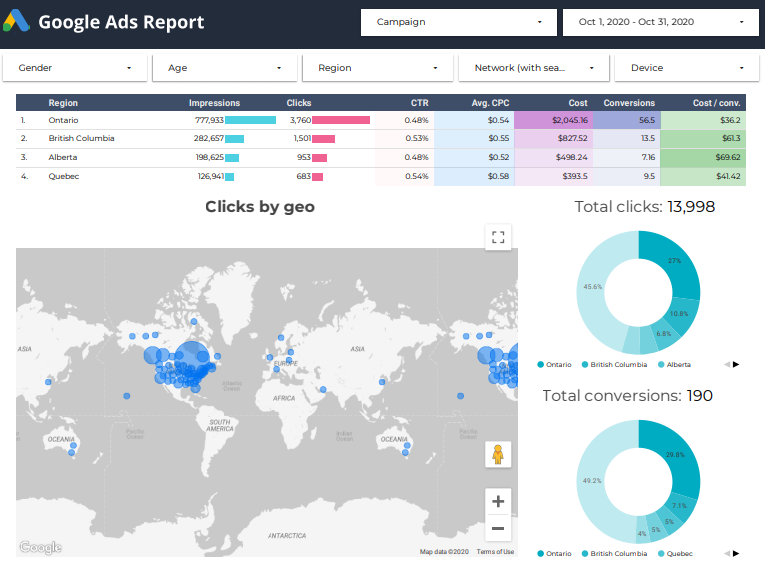
It is essential to know what countries or cities perform better when it comes to location targeting. PromoNavi’s PPC Report for Google Data Studio provides you with all the data you need to uncover the best/worst locations for targeting.
Here is a comprehensive manual on setting up and using PromoNavi’s GDS report. Do you need more reports? Read on our blog post—”15 Best PPC Reports for GDS.”
#7: Not Geofencing Your Ads
In geofencing, a virtual barrier is created around a physical location. The barrier has a shape of a circle (or several crossing circles) covering the selected location.
This will provide you with a high level of accuracy that will help you understand the effects of different geo-targeting campaigns, including those on Google Ads.
For multinational businesses, advertising is all about efficiency—you need to ensure that your campaigns reach the right local customers, not overlap. Geofencing is considered the best way to do this—for example, with Facebook or Google—to establish clear geographic areas. The campaign will target these areas only.
Geofencing also refers to advertising when someone enters this barrier—that person may receive a push notification, an ad, or an alert in your mobile app, based on the location and distance from the business. Today, geofencing is one of the most used strategies for specific location-based ads.
#8: Not Monitoring All Of Your Pages
Of course, it’s not easy to keep track of everything that happens on review sites like TripAdvisor or Yelp for even a single location business. When you bring in multiple locations for the same, the task quickly becomes daunting.
While it’s not easy, it’s very important that you keep monitoring and managing all your pages through various online platforms. In this aspect, timing matters a lot. For instance, if someone visits one of your business locations and leaves a bad review, it could easily affect your entire business.
Hence, the only way to manage and deal with these issues is to ensure that you are actively engaging these pages to become immediately aware of any issues and send a reply just as quickly.
#9: Not Setting Up “Google My Business” Correctly
It’s essential that Google My Business is set up correctly. While it may seem very trivial, the impact can be very extensive. Today, customers and clients use searches and social media to look for and research local businesses; they have now become important key channels. If your location is not lined up properly in your platform’s back-end system, it could mean bad news for you and your business.
Google (and Facebook, for that matter) must know which master account is being used to control different locations and make changes and manage the settings. If done correctly, you will be able to unlock many significant options, like targeting online ads with greater efficacy or publishing content on different pages.
#10: Inconsistent Branding Across Different Locations
Inconsistent branding is often considered a rookie mistake. Proper branding has been a topic for discussion for a long time, and both sides have significant support. However, we would like to say that you should bid on your own brand’s keywords to increase conversions. However, this also means you will have to keep a closer eye on your brand’s overall value.
Of course, you would want each of your locations to have its presence; however, it is also crucial that branding remains consistent. This matters for two main reasons—first, you need to ensure that your brand’s value is carried across different locations. If the client/customer had a good experience in one location, you would want them to see and recognize your brand’s name and logo in another location and make the obvious connection.
Let’s say you have two stores located in New York and Los Angeles. A customer in New York has received a bad experience, and that resentment will likely carry on when that customer visits the Los Angeles branch as well, and vice versa.
Second, most online platforms like review sites and search engines tend to be very selective about linking locations with one another. This means that even if there is a minute setback—like calling one location “ABC, Inc” and the other “The ABC, Inc”—you can lose those valuable associations.
#11: Setting Up Locations that Do Not Scale
If you have more than a single office or store that offers the same products and services, it only makes sense that you create a single platform to manage all of the locations. However, the problem with online platforms and search engines is that they do not understand these systems, as they are generally made to provide customers with information related to specific locations.
Hence, you shouldn’t set up locations that won’t eventually scale. This doesn’t imply that you create a separate platform for each location. However, you should ensure that your branches have their own pages within the platform, with additions like reviews, offers, images, addresses, and phone numbers.
Final Thoughts
Geo-targeting in Google Ads is an impressive feature that allows you to target specific markets in districts, cities, states, and countries. Perhaps the best aspect here is that you don’t even need a physical business location.
Any marketing campaign can be a tricky situation to manage. While it is possible to generate fantastic results, it can also blow up on your face and waste money and time. Hence, it is essential to understand your customers based on their demographics.
When people look for services and products ‘near me,’ it typically means they’re ready to buy. For most people, shopping is done online. If you can combine the ‘to buy’ and ‘near me’ intent, you will usually get positive results. However, if you want to succeed and have the best results possible, ensure that you avoid the mistakes mentioned above and use the proper tools that help you get the most out of your Google Ads campaigns.